Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -Ga
-Ga O
O (001)
(001)Tsai, Y. H.*; Kobata, Masaaki; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tanida, Hajime; Kobayashi, Toru; Yamashita, Yoshiyuki*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(11), p.112105_1 - 112105_5, 2024/03
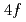 states in the electronic structure of the intermediate-valence superconductor CeIr
states in the electronic structure of the intermediate-valence superconductor CeIr
Fujimori, Shinichi; Kawasaki, Ikuto; Takeda, Yukiharu; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Sasabe, Norimasa*; Sato, Yoshiki*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Nakamura, Ai*; Maruya, A.*; Homma, Yoshiya*; et al.
Electronic Structure (Internet), 5(4), p.045009_1 - 045009_7, 2023/11
 Al
Al ; Impact of the U
; Impact of the U 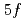 states on the electronic structure of UPd
states on the electronic structure of UPd Al
Al
Fujimori, Shinichi; Takeda, Yukiharu; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Posp
 il, J.*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Haga, Yoshinori
il, J.*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Haga, Yoshinori
Physical Review B, 105(11), p.115128_1 - 115128_6, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao
Photon Factory Activity Report 2016, 2 Pages, 2017/00
In order to elucidate the adsorption states of radioactive Sr-90 in soil, chemical bonding states of non-radioactive strontium adsorbed on layered oxide (mica) have been investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy. Since the number of atoms in radioactive Sr-90 is extremely small, the XPS and XANES were measured under total reflection condition of the incident X-rays. The detection limit in total reflection XPS was about 150 pg/cm , which corresponds to 300 Bq of Sr-90. The Sr 2p
, which corresponds to 300 Bq of Sr-90. The Sr 2p core-level energy in XPS shifted to lower energy with the decrease in the thickness of Sr layer. Also, the Sr 2p
core-level energy in XPS shifted to lower energy with the decrease in the thickness of Sr layer. Also, the Sr 2p
 Sr 4d
Sr 4d resonance energy in XANES shifts to lower energy with the decrease in the thickness. On the basis of a simple point charge model, it was elucidated that the chemical bond between Sr and mica surface becomes ionic with the decrease in the adsorbed amount of strontium.
resonance energy in XANES shifts to lower energy with the decrease in the thickness. On the basis of a simple point charge model, it was elucidated that the chemical bond between Sr and mica surface becomes ionic with the decrease in the adsorbed amount of strontium.
Okane, Tetsuo; Kobata, Masaaki; Sato, Isamu*; Kobayashi, Keisuke*; Osaka, Masahiko; Yamagami, Hiroshi
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 297, p.251 - 256, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Izumi, Toshinori
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 13, p.417 - 421, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:1The interaction between alkali metals and oxides has attracted much attention as heterogeneous catalysis, chemical reaction promoters, and high intensity electron emitter. Also the interaction of cesium and oxides has become important subject, because radioactive cesium trapped in minerals such as clay and soil may cause health risks. In the present study, we analyzed chemical states of ultra-trace amount of cesium on oxide surfaces by total reflection X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (TR-XPS) exited by synchrotron radiation. For the adsorbed cesium thicker than 0.01 layer, cesium is weakly bound with oxide through Van-der-Waals force. On the other hand, for ultra-thin layer about 0.002 layer, the chemical bond changes to covalent bond. It is suggested that this change in the chemical bonding state is one of the reasons why radioactive cesium is hard to be released from minerals.
 7 surface at 300 K; Comparison of thermal equilibrium gas and supersonic molecular beams for oxygen adsorption
7 surface at 300 K; Comparison of thermal equilibrium gas and supersonic molecular beams for oxygen adsorptionYoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 118(18), p.9436 - 9442, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:38.22(Chemistry, Physical)Translational energy of gas molecules is a fundamental physical quantity in gas-solid reactions. Understanding adsorption process of thermal gas in terms of translational energy remains an unsolved issue. Here, for thermal-O and supersonic O
and supersonic O molecular beams, we present a comparative study of oxide evolution at a Si(111)-7
molecular beams, we present a comparative study of oxide evolution at a Si(111)-7 7 surface at room temperature. Real-time observations of oxides were conducted by employing synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy. It was found that ins structure is the common first product for oxidation by thermal-O
7 surface at room temperature. Real-time observations of oxides were conducted by employing synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy. It was found that ins structure is the common first product for oxidation by thermal-O and supersonic O
and supersonic O molecular beams. Similarities between them for oxide evolution were found and illustrate the notion that translational energy of thermal O
molecular beams. Similarities between them for oxide evolution were found and illustrate the notion that translational energy of thermal O can be ascribed to the average molecular kinetic energy defined based on the most probable speed of the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution. This experimental result suggests that translational energy is the unifying reaction parameter that rationalizes adsorption mechanisms.
can be ascribed to the average molecular kinetic energy defined based on the most probable speed of the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution. This experimental result suggests that translational energy is the unifying reaction parameter that rationalizes adsorption mechanisms.
Yokoya, Akinari; Fujii, Kentaro; Ushigome, Takeshi; Shikazono, Naoya; Urushibara, Ayumi; Watanabe, Ritsuko
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 122(1-4), p.86 - 88, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:60.27(Environmental Sciences)We have studied yields of DNA damages induced by soft X-rays obtained from a conventional soft X-ray machine in a LET region between  -rays and ultrasoft X-rays. Practically soft X-rays with a broad energy spectrum emitted from a target of heavy metal, such as tungsten, have been widely used not only for radiobiological experiments but also for medical application such as mammography. Radiation weighting factors for these soft X-rays have been assigned to be 1 by ICRP. However, the fraction of a large number of low energy photons in the spectrum (below several tens keV) provided by bremsstrahlung is expected to be more effective for DNA damage induction than
-rays and ultrasoft X-rays. Practically soft X-rays with a broad energy spectrum emitted from a target of heavy metal, such as tungsten, have been widely used not only for radiobiological experiments but also for medical application such as mammography. Radiation weighting factors for these soft X-rays have been assigned to be 1 by ICRP. However, the fraction of a large number of low energy photons in the spectrum (below several tens keV) provided by bremsstrahlung is expected to be more effective for DNA damage induction than  -rays since low energy photo- and Auger electrons predominantly ejected in consequence of a photoelectric effect can produce dense clusters of ionization/excitation on DNA molecules. We have examined the yield of DNA strand breaks induced by white soft X-rays (150 kVp, tungsten target). Yields of base lesions revealed by base excision repair enzymes will be also presented.
-rays since low energy photo- and Auger electrons predominantly ejected in consequence of a photoelectric effect can produce dense clusters of ionization/excitation on DNA molecules. We have examined the yield of DNA strand breaks induced by white soft X-rays (150 kVp, tungsten target). Yields of base lesions revealed by base excision repair enzymes will be also presented.
Inoue, Takashi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Taniguchi, Masaki; Dairaku, Masayuki; Hanada, Masaya; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Sakamoto, Keishi
Nuclear Fusion, 46(6), p.S379 - S385, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:74.54(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The JAERI MeV accelerator has been designed extrapolating vacuum insulation design guidelines (the clump theory and Paschen law) to Mega Volt and long vacuum gap. Reduction of electric field concentration at triple junction by a large stress ring was effective to prevent flashover along insulator surface. By the vacuum insulation technology above, the accelerator sustained 1 MV for 8,500 s continuously. Strong enhancement of negative ion surface production has been attained by stopping vacuum leaks due to SF permeation through Viton O rings and a damage of port by backstream ions, followed by increase of the H
permeation through Viton O rings and a damage of port by backstream ions, followed by increase of the H ion current density without saturation. Operating the KAMABOKO source with high power arc discharge (
ion current density without saturation. Operating the KAMABOKO source with high power arc discharge ( 40 kW), H
40 kW), H ion beams of 146 A/m
ion beams of 146 A/m (total ion current: 0.2 A) have been obtained stably at the beam energy of 836 keV (pulse length:
(total ion current: 0.2 A) have been obtained stably at the beam energy of 836 keV (pulse length:  0.2 s). Bremsstrahlung generation in the accelerator is also estimated from EGS4 analysis, and then discussion on the breakdown possibility follows.
0.2 s). Bremsstrahlung generation in the accelerator is also estimated from EGS4 analysis, and then discussion on the breakdown possibility follows.
Minehara, Eisuke
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 557(1), p.16 - 22, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:60.27(Instruments & Instrumentation)The JAERI FEL facility at Tokai, Ibaraki, Japan has been well known one of the two existing and operating superconducting energy recovery linacs together with one more of JLAB (Jefferson national accelerator facility) FEL facility at Newport News, Virginia, U.S.A. We have independently and successfully developed one of the most advanced and newest accelerator technologies named "superconducting energy recovery linacs (ERLs)" and the application technologies using ERLs in future. We plan to report the current high power FEL upgrade program research, stress corrosion cracking prevention technology research, large current and high brightness photoelectron gun research of negative-electron affinity (NEA) photocathode and NEA electron-excitation cathode as the most important elemental technology in realizing many powerful ERLs.
Takakuwa, Yuji*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
Shokubai, 47(5), p.352 - 357, 2005/08
Oxidation reactions of Ti(0001) surfaces were monitored by real-time photoelectron spectroscopy with high brilliant synchrotron radiation and He-I resonance line. An oxygen adsorption model and ultra-thin oxide layers formation processes were reviewed on the basis of time evolutions of the adsorbed oxygen amount, oxidation states, electronic states and the work function, which were obtained from photoelectron spectra for Ti 2p and O 1s core levels as well as the valence band.
Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio; Hirabayashi, Takakuni*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(9), p.919 - 924, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:61.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new laser decontamination method utilizing a gel made from a sodium silicate solution and an acid was developed for removing radioactive nuclide incorporated into a surface oxide layer on metal waste. Decontamination tests were carried out using both simulated contaminated samples and pipe specimens cut from the primary coolant system of the Japan Power Demonstration Reactor. In the case of surface oxide layer consisting mainly of iron oxide, more than 99% of surface radioactivities were removed after two to three decontamination runs. In order to ascertain the role of laser irradiation on chemical reactions, chemical states of O and Fe in the oxide layer before and after decontamination were analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. It was found that the oxide layer was dissolved into the acid-containing gel, and the reaction was extensively promoted by the laser irradiation.
Sasaki, Masayoshi*; Morimoto, Yasutomi*; Kimura, Hiromi*; Takahashi, Koji; Sakamoto, Keishi; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Okuno, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(Part1), p.899 - 903, 2004/08
A CVD diamond has been the reference material of a torus widow for a rf heating system in a fusion reactor. Since the window is in the circumstance of tritium, helium and radio activated dust, it is important to elucidate the effect of ions on chemical structure of the diamond, existing states of tritium and tritium inventory. Polycrystalline CVD diamond disks( =10.0mm, t=0.21mm) used in this study are the same grade as rf windows. After sputtering the surface with 1.0 keV Ar
=10.0mm, t=0.21mm) used in this study are the same grade as rf windows. After sputtering the surface with 1.0 keV Ar to remove oxygen impurity, the sample was irradiated with deuterium (D
to remove oxygen impurity, the sample was irradiated with deuterium (D
 ) or helium ions (He
) or helium ions (He ) at an angle of 0 degrees to the surface normal. The irradiation energies of deuterium and helium are 0.25 keV D
) at an angle of 0 degrees to the surface normal. The irradiation energies of deuterium and helium are 0.25 keV D and 0.45 keV He
and 0.45 keV He , respectively. The structural change of the irradiated sample was measured by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) technique. The C1s peak shift toward lower binding energy side was observed when deuterium ions irradiated. This result indicates that the diamond changes to amorphous carbon due to formation of C-D bond.
, respectively. The structural change of the irradiated sample was measured by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) technique. The C1s peak shift toward lower binding energy side was observed when deuterium ions irradiated. This result indicates that the diamond changes to amorphous carbon due to formation of C-D bond.
Matsushita, Tomohiro*; Agui, Akane; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Europhysics Letters, 65(2), p.207 - 213, 2004/01
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:76.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A "scattering pattern matrix" method is proposed here to overcome the difculties presented by photoelectron holography, such as forward-scattering and multi-energyproblems. This method makes it possible to reconstruct a three-dimensional atomic arrangement from a single-energy hologram. We have utilized the "scattering pattern matrix" that includes the angular variation of the scattered object waves, and we have adopted a specialaverage process and the gradient projection method for minimizing the mean-squared error. The reconstruction of the Si bulk structure is demonstrated by using an experimental Si(111) 2s single-energy hologram.
Takakuwa, Yuji*; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Mizuno, Yoshiyuki*; Tonda, Hideki*; Homma, Teiichi*
Hyomen Kagaku, 24(8), p.500 - 508, 2003/08
Temperature dependence of the initial oxidation kinetics of Ti(0001) surface was investigated by low energy electron diffraction (LEED) and real-time photoelectron spectroscopy. The LEED observation revealed that the oxide layers grew epitaxially. From the oxygen uptake curve, it was clarified that oxigen diffusion was significantly enhanced by surface temperature and the oxide layers thickness reached to 7 nm at 400 C. From Ti-2p photoelectron spectroscopy, TiO
C. From Ti-2p photoelectron spectroscopy, TiO was predominant at the subsurface while TiO and Ti
was predominant at the subsurface while TiO and Ti O
O components were also observed at the interface.
components were also observed at the interface.
Takakuwa, Yuji*; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro*; Mizuno, Yoshiyuki*; Tonda, Hideki*; Homma, Teiichi*
Applied Surface Science, 216(1-4), p.395 - 401, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:64.2(Chemistry, Physical)Real-time in-situ observation using photoelectron spectroscopy for elementary processes of Ti(0001) oxidation by O molecules has been performed at the surface reaction analysis apparatus installed at the BL23SU in the SPring-8. And the real-time observation has been also performed by RHEED-AES methods at Tohoku University. The partial pressure region of oxygen was from 2x10
molecules has been performed at the surface reaction analysis apparatus installed at the BL23SU in the SPring-8. And the real-time observation has been also performed by RHEED-AES methods at Tohoku University. The partial pressure region of oxygen was from 2x10 Torr to 8x10
Torr to 8x10 Torr. The surface temperature was 473 K and 673 K. The variation from clean Ti surface toward TiO
Torr. The surface temperature was 473 K and 673 K. The variation from clean Ti surface toward TiO was comfirmed by observation of Ti-2p and O-1s photoelectron spectra. Reflected electron intensity and O-KLL Auger electron intensity oscillated in the RHEED-AES measurements. These facts revealed that the surface morphological change of the oxidized Ti(0001) surface was associated not only with a disappearance of the surface metallic layer but also with a change of the oxidation state.
was comfirmed by observation of Ti-2p and O-1s photoelectron spectra. Reflected electron intensity and O-KLL Auger electron intensity oscillated in the RHEED-AES measurements. These facts revealed that the surface morphological change of the oxidized Ti(0001) surface was associated not only with a disappearance of the surface metallic layer but also with a change of the oxidation state.
Takakuwa, Yuji*; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Mizuno, Yoshiyuki*; Tonda, Hideki*; Homma, Teiichi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 200, p.376 - 381, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.43(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
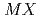 (
( =Pt, Pd;
=Pt, Pd; 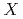 =P, As, Sb)
=P, As, Sb)Iwasaki, T.*; Sekiyama, Akira*; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Okazaki, Makoto*; Kadono, Koji*; Utsunomiya, Hiroshi*; Imada, Shin*; Saito, Yuji; Muro, Takayuki*; Matsushita, Tomohiro*; et al.
Physical Review B, 65(19), p.195109_1 - 195109_9, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:71.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 and V
and V O
O after rare-gas sputtering
after rare-gas sputteringSasaki, Teikichi; Baba, Yuji; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Sasase, Masato*; *
Surface and Interface Analysis, 20, p.682 - 686, 1993/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:21.43(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Baba, Yuji; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Sasaki, Teikichi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 66, p.424 - 432, 1992/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:60.99(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English